Modern Cosmology
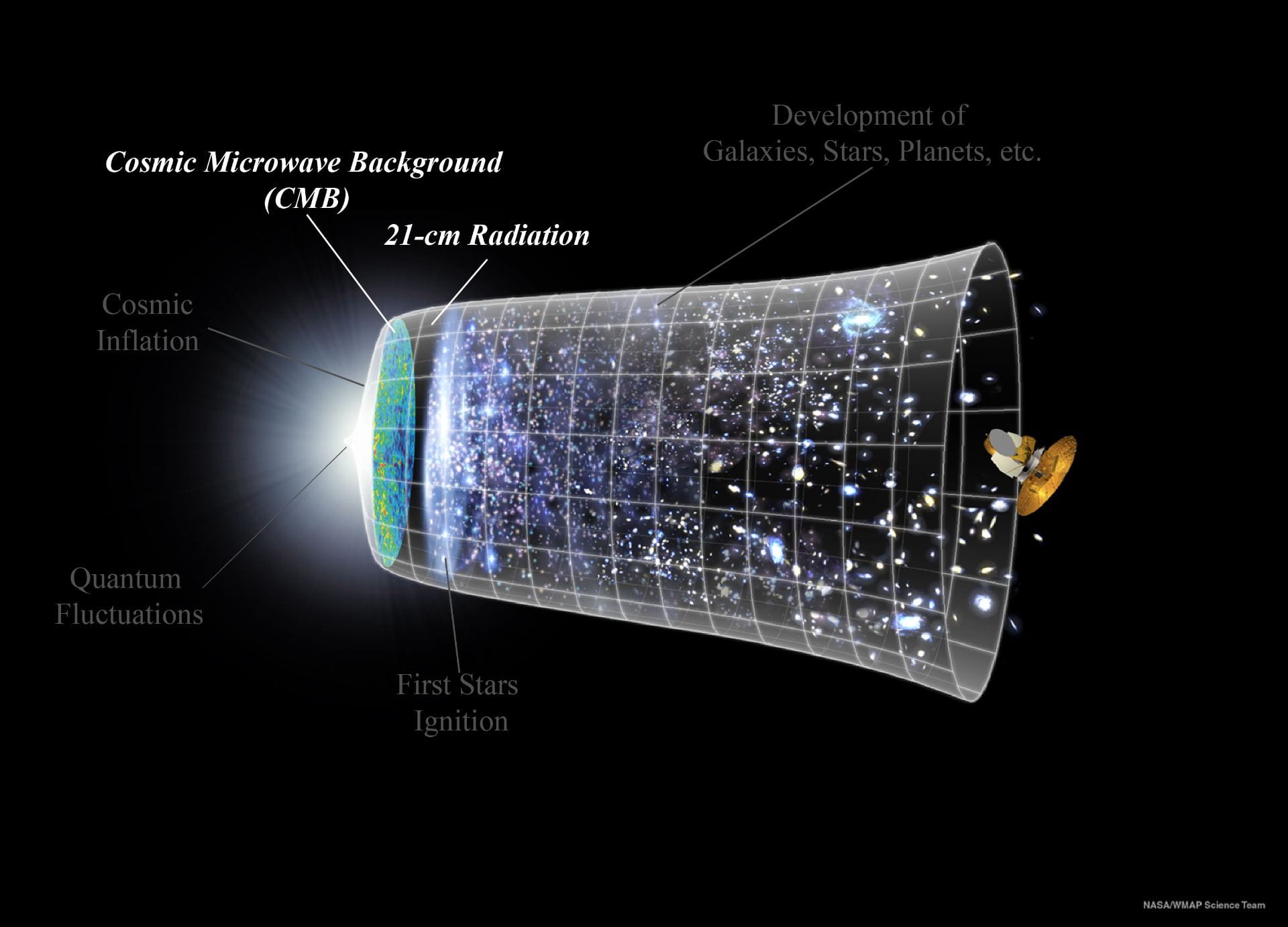 History of the Universe. Original figure by NASA WMAP team, edited by Zhilei Xu
History of the Universe. Original figure by NASA WMAP team, edited by Zhilei Xu
I am interested in studying the universe mainly via observing the 21-cm radiation and the cosmic microwave background (CMB). Since both of them were emitted in the early universe, they carry critical information of the universe's history.
1. 21-cm Observations
Hydrogen Epoch of Reionization Array (HERA)
 Hera 19 complete, Feb. 2016. Photo credits: HERA Collaboration
Hera 19 complete, Feb. 2016. Photo credits: HERA Collaboration
I am a member of the HERA collaboration (link) to study the Epoch of Reionization by observing the radiation from high-redshift neutral hydrogen emission.
We have developed an algorithm to map the interferometric data with robust statistics, called direct optimal mapping (GitHub link).
Z. Xu, et al., Direct Optimal Mapping Image Power Spectrum and its Window Functions, arXiv:2311.10711, The Astrophysical Journal (in review), 2023
Z. Xu, et al., Direct Optimal Mapping for 21cm Cosmology: A Demonstration with the Hydrogen Epoch of Reionization Array, The Astrophysical Journal 938:128, 2022
We are using these map products to study the epoch of reionization, including measuring the power spectra in image space and cross-correlating the maps with other cosmological datasets.
2. Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB)
2.1 Cosmology Large Angular Scale Surveyor (CLASS)
 CLASS telescopes Observing at the Atacama Desert. Photo credits: CLASS Collaboration
CLASS telescopes Observing at the Atacama Desert. Photo credits: CLASS Collaboration
I am a member of the team that designed and built the Cosmology Large Angular Scale Surveyor (CLASS). In graduate school, I designed and integrated the 40GHz telescope and led the calibration analysis after its deployment. After graduation, I am advising the calibration analysis for the following telescopes. Part of the results are presented in the following publications:
Z. Xu, M. K. Brewer, P. F. Rojas, Y. Li, K. Osumi, B. Pradenas, et al. Two-year cosmology large angular scale surveyor (CLASS) observations: 40 GHz telescope pointing, beam profile, window function, and polarization performance. The Astrophysical Journal, 891(2):134, Mar 2020;
J. W. Appel, Z. Xu, I. L. Padilla, K. Harrington, B. P. Marquez, et al. On-sky performance of the CLASS q-band telescope. The Astrophysical Journal, 876(2):126, May 2019;
Z. Xu. Cosmology Large Angular Scale Surveyor (CLASS): Integration and Testing of CLASS at 40 GHz. PhD thesis, Johns Hopkins University, Aug 2017.
2.2 Simons Observatory (SO)
 Working in the LATR. Photo credits: Eric Sucar
Working in the LATR. Photo credits: Eric Sucar
In the Simons Observatory (SO), I worked with the University of Pennsylvania team to design, manufacture, integrate, and test the Large Aperture Telescope Receiver (LATR) as the lead postdoc. The LATR is the largest cryogenic receiver with a < 100mK cryogenic stage. I gave a tour of the instrument in this video (link). The design and testing results are presented in the following publications:
Z. Xu, et al. The Simons Observatory: the Large Aperture Telescope (LAT). Research Notes of the AAS, Volume 5, Number 4, April 2021;
Z. Xu, T. Bhandarkar, G. Coppi, A. Kofman, J. L. Orlowski-Scherer, N. Zhu, et al. The Simons Observatory: the Large Aperture Telescope Receiver (LATR) Integration and Validation Results. In Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, volume 11453, December 2020;
SPIE page (link) with the paper and the presentation
Z. Xu, G. Chesmore, et al. The Simons Observatory: Metamaterial Microwave Absorbers (MMA) and the Cryogenic Applications, accepted by Applied Optics, Oct. 2020;
Editor's pick with press release at The Optical Society (OSA) and Penn Today. This work is also mentioned in New York Times.
N. Zhu, J. L. Orlowski-Scherer, Z. Xu, et al. Simons Observatory large aperture telescope receiver design overview. In Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, volume 10708, page 1070829, July 2018;
J. L. Orlowski-Scherer, N. Zhu, Z. Xu, et al. Simons Observatory large aperture receiver simulation overview. In Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, volume 10708, page 107083X, July 2018;
G. Coppi, Z. Xu, et al. Cooldown strategies and transient thermal simulations for the Simons Observatory. In Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, volume 10708, page 1070827, July 2018.
In addition to the LATR instrumentation, I also lead the calibration analysis in the SO pipeline working group (PWG) focusing on the beam, calibration, and polarization calibration of the instrument.
I also co-chair the Talks Panel within the Simons Observatory.
2.3 CMB-S4
 Figure credits: CMB-S4 Collaboration
Figure credits: CMB-S4 Collaboration
I work in the Large Aperture Telescope (LAT) and Large Aperture Telescope Receiver (LATR) working groups within CMB-S4 in instrumentation.
I also served on the CMB-S4 Governing Board (GB) as the postdoc representative.
3. Cross-correlation
I am interested in cross-correlating different data sets, including galaxy surveys, CMB data sets, 21 cm data etc., to understand the history of the universe and the evolution of the galaxies. One initial work we did by cross-correlating the Planck and Dark Energy Survey (DES) data sets was published in:
S. Pandey, E. J. Baxter, Z. Xu, et al. Constraints on the redshift evolution of astrophysical feedback with sunyaev-zel’dovich effect cross-correlations. Phys. Rev. D, 100:063519, Sep 2019.
